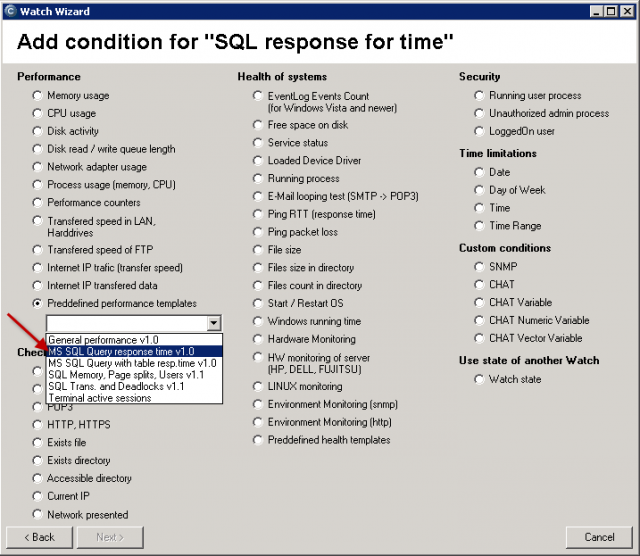
MS SQL performance by measuring of time
The optimal way how to get the total MS SQL server's performance is to measure time of an operation, which is similar to the one executed by the application running over MS SQL. In other words, query the SQL server for certain information, or make unified operations directly in the application's database (we assure you, that these are absolutely safe toward data in the database and application)
There are two "performance" templates for measuring of time over MS SQL available :
1. MS SQL Query Response time - measures time of operation sequence :
connection to the database,
requesting system time from the SQL server
disconnection from the SQL server
Setup procedure (below in the article)
2. MS SQL Query Response time with table - measures time of operation sequence :
connection to the database,
creation of a table with 300 rows and 5 columns, which it'll fill with the current date
deletes this table
disconnection from the database
Setup procedure (below in the article)
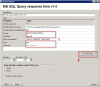
1. Setup procedure to MS SQL Query Response time
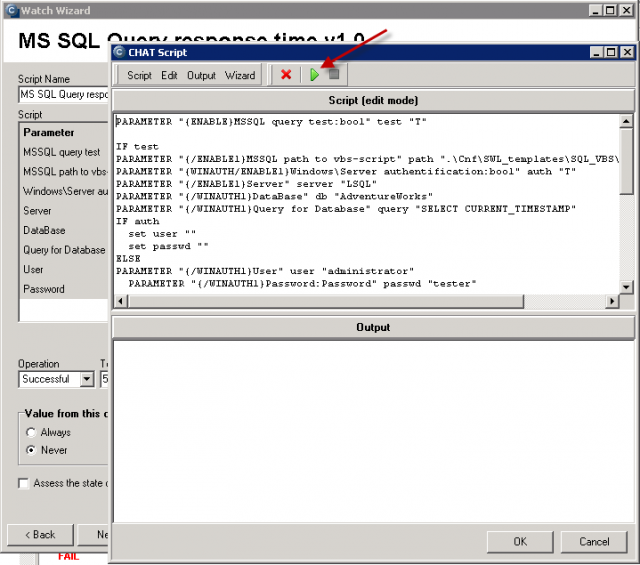
Watch measures time of this operation sequencemeria čas sledu operácií :
connection to the database,
requesting system time from the SQL server
disconnection from the SQL server
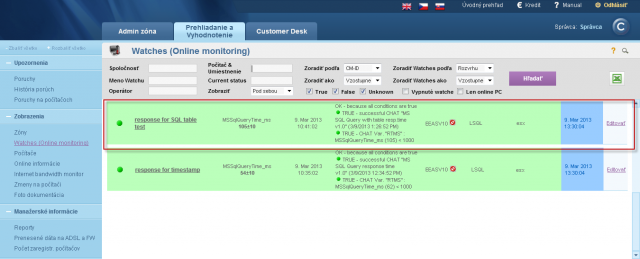
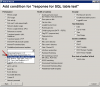
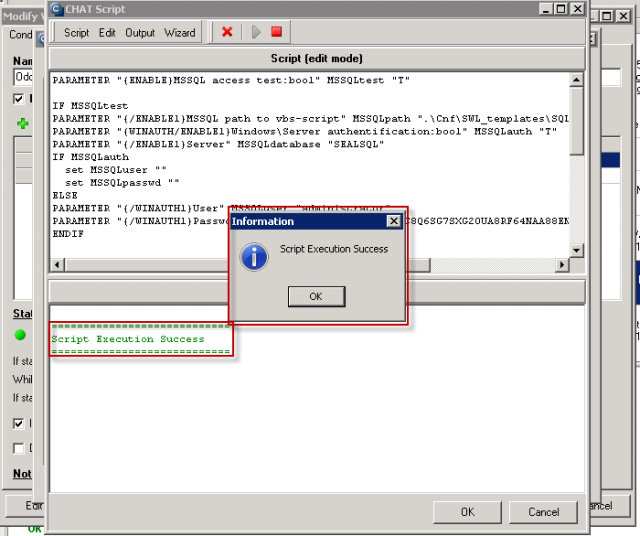
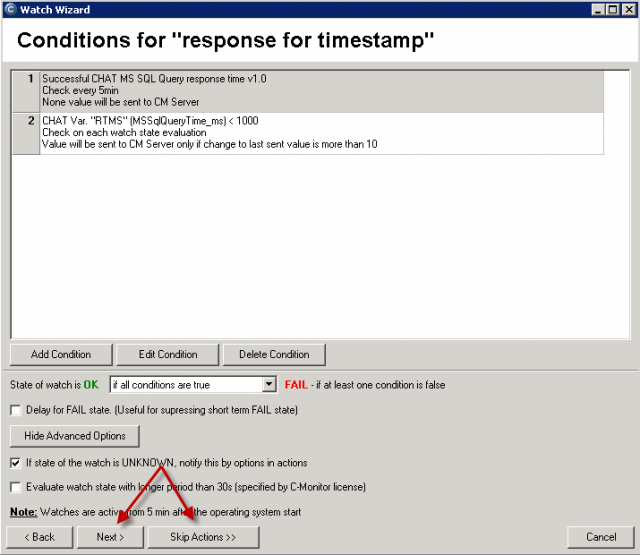
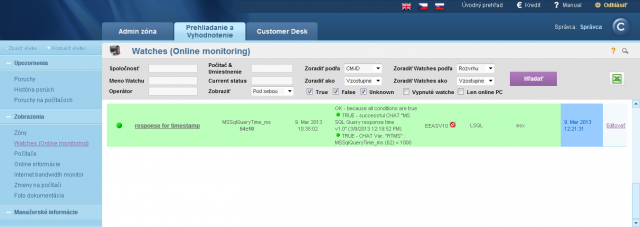
The result (value) is the time of operations in miliseconds, which is transferred for view and history archivation to CM Portal. A great value is around 50ms, but it may vary according to HW and version of the SQL server. Even a response higher by just +20% indicates a significant load, since the test consists of relatively quickly executable operations. You should empirically determine the value, at which your applications run fast, and when the system is getting slow, and set the Watch's limit value accordingly.
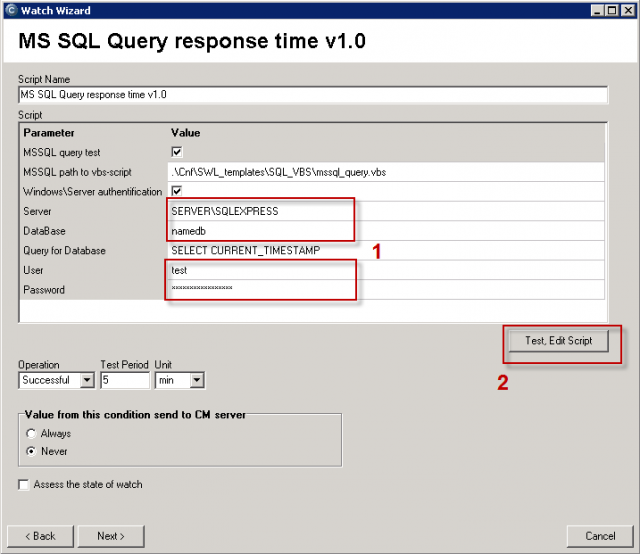
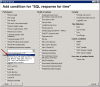
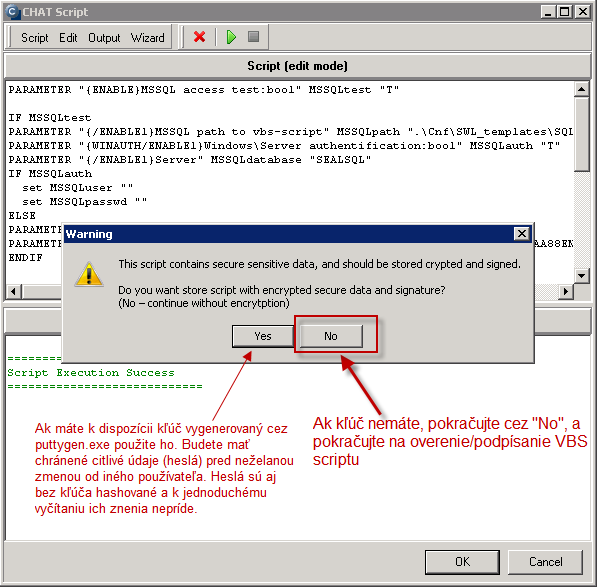
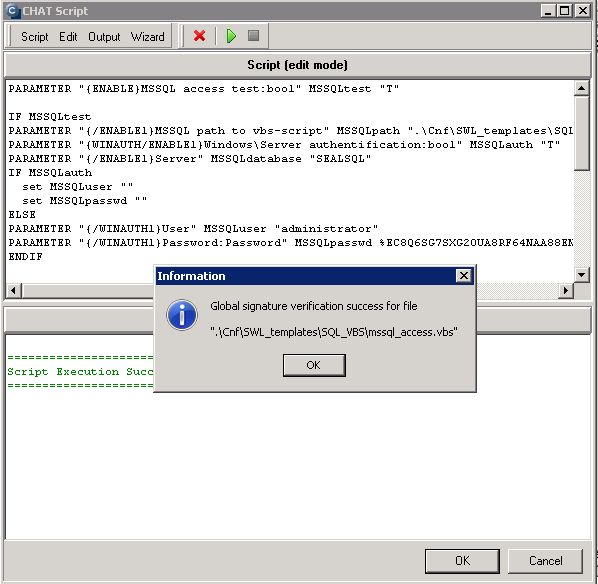
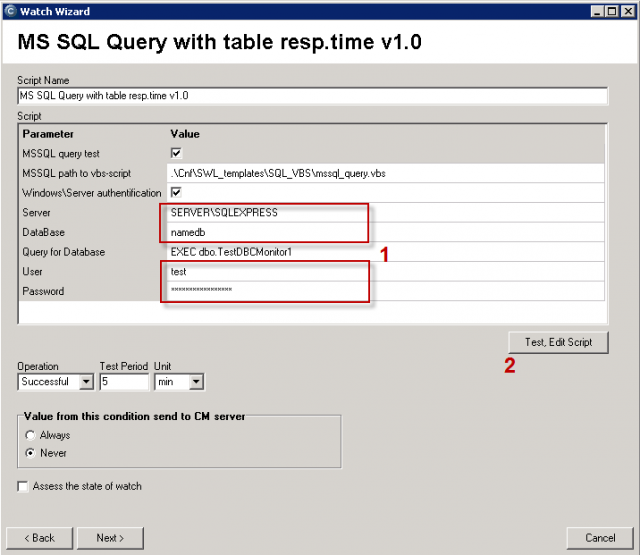
You must choose name of the SQL server, or instance, according to type of installation. For the first SQL instance with default configuration, type one of these alternatives into the field Server :
1. server's network name
2. server's network name\ name of instance (the instance name, if there's only one, is usually MSSQLSERVER or SQLSERVER or possibly SQLEXPRESS).
For other instances, write name of the service for the SQL server's instance in the form MSSQL$instance_name.
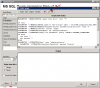
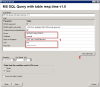
2. Setup procedute to MS SQL Query Response time with table (table operations)
measures time of this operation sequence :
connection to the database,
creation of a table with 300 rows and 5 columns, which it'll fill with the current date
deletes this table
disconnection from the database
The result (value) is the time of operations in miliseconds, which is transferred for view and history archivation to CM Portal. A great value is around 100ms. When the SQL server is loaded, the value can reach up to 500ms, which already signalizes reaction slowdown of the application that runs on the given server.
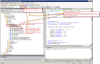
This section only describes the differences toward the above stated procedure. The main difference is that work with the table is realized by an SQL procedure, which has to be imported to the SQL server. The procedure is distributed in a C-Monitor installation file stored at
drive:\CMonitor\Cnf\SWL_templates\SQL_VBS\sql_table_procedure_v1xx.sql.
Import of the procedure to the SQL server
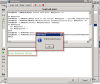
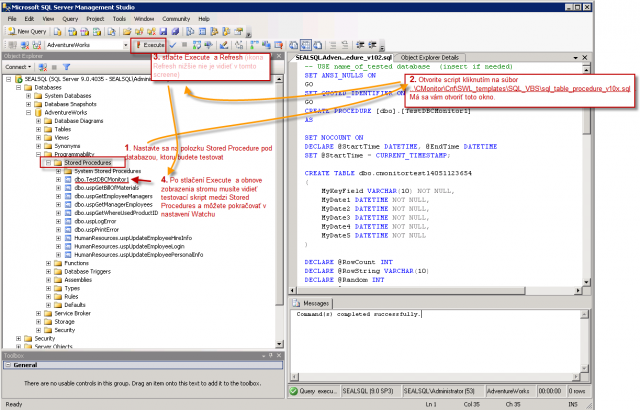
1. Open SQL management console
2. In hierarchy of SQL objects to SQL server, go to server / databases / your_database / Programmability / Stored Procedures
3. Doubleclick to open procedure
drive:\CMonitor\Cnf\SWL_templates\SQL_VBS\sql_table_procedure_v1xx.sql.
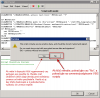
4. Press Execute
5. Refresh the tree and check if this procedure was added under your database into Stored Procedures
dbo.TestDBCMonitor1
4. Close SQL management console
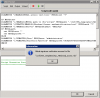
Tip : It might occur, that the procedure will be saved under System databases / Master. You should then open the procedure's file from C-Monitor - sql_table_procedure_v1xx.sql and use the command USE in the first line.
The original text is :
-- USE name_of_tested database (insert only if needed and delete double dash at start of this row)
rewrite it to :
USE name_of_your_database
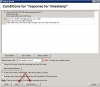
Continuation of Watch settings is the same as in the first case
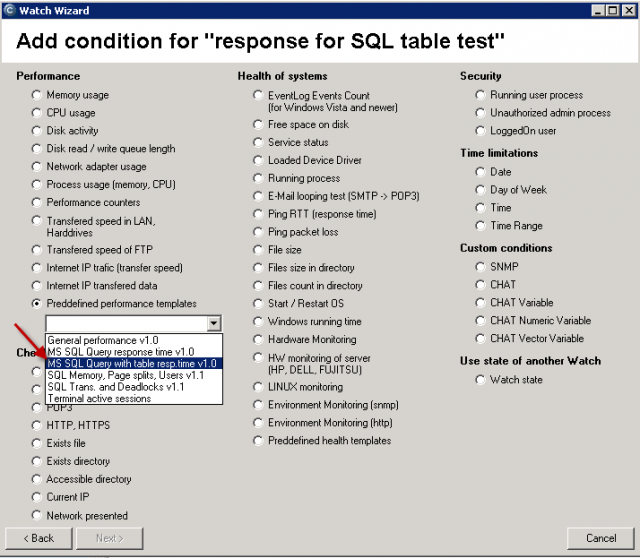
Only the template selection is different, other steps are identical
Continue according to the above stated procedure.